Thesis
Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Co., Ltd. (NYSE:TSM) is the largest contract manufacturer of chips, holding an impressive market share of approximately 54%. Its business model is unparalleled as it addresses the risk associated with having designers manufacture their chips in-house, which would potentially lead to competition from Integrated Device Manufacturers (IDMs) who are also designers. This strategic advantage is likely to solidify TSMC’s position as the leading contract manufacturer. Projections indicate that TSMC’s revenue will grow at a rate of around 12% from 2025 to 2028.
To assess the value of TSMC, I employed a Discounted Cash Flow [DCF] model that factored in the possibility of TSMC reducing its net income margin and maintaining high capital expenditures. The DCF analysis yielded a present price of $123.43, representing an upside potential of approximately 23% from the current stock price of $100.23. Subsequently, I projected the present price into the future, arriving at a target price of $184.52 for 2028, which indicates a significant upside of around 84%.
I am confident in my decision to invest in TSMC since even if their outlook is revised downward, it presents an opportunity to acquire more shares. TSMC’s enduring value as a company makes it a worthy investment option in my opinion.
Overview
TSMC’s Story
The development of the semiconductor industry encounters three primary challenges: high costs, a scarcity of qualified professionals, and the risk of rapid advancements rendering existing semiconductors obsolete within a short timeframe.
In order to nurture the technological sector on the island, the Taiwanese government has extended special tax incentives to these emerging companies, subjecting them to an exceptionally low tax rate of 1%. Moreover, the government has offered public funding and assumed some of the risks by becoming a stakeholder. Additionally, universities have been encouraged to collaborate with these companies, allowing students to gain practical experience and fostering ongoing partnerships beyond their studies.
TSMC was established in the 1990s, with the Taiwanese government acquiring a 48% stake in the company. To comprehend TSMC’s business model, it is crucial to understand the concept of Integrated Device Manufacturers [IDMs] such as Intel Corporation (INTC), who traditionally designed and manufactured their own chips, embodying vertical integration. However, with the exponential increase in demand for semiconductors, IDMs faced challenges, particularly in adapting their manufacturing processes to new designs. As previously mentioned, the rapid advancement of semiconductor technology further exacerbated this issue.
To address the inflexibility in production, semiconductor companies began outsourcing their chip designs to IDMs, who were also designers themselves. This arrangement created a rivalry between the designers and the IDMs, posing the risk of technology theft if the IDM acted in bad faith. It was within this context that Morris Chang, an experienced professional in the semiconductor market, founded TSMC. TSMC became the first company to exclusively focus on semiconductor manufacturing, without involvement in design or commercialization. By specializing solely in manufacturing, TSMC could adapt its structure to accommodate designs from various designer companies. This flexibility offered a sense of security to designers, as TSMC did not present a risk of stealing their intellectual property.
This characteristic forms TSMC’s economic moat, making it a formidable competitor even for Intel. Unlike Intel, which operates as an IDM, TSMC provides a trusted environment for designers to safeguard their designs. While some may argue that Intel would not engage in such practices, the potential recourse for designers would involve pursuing legal action against Intel, a process that would be time-consuming and costly. Therefore, in this scenario, prevention is preferable to finding a cure.
The China Risk
It is widely known that Berkshire Hathaway, Inc. (BRK.A) (BRK.B), led by Buffett, made a notable purchase of approximately $4.1 billion worth of TSMC’s stock during the third quarter of 2022. However, they subsequently sold 90% of their stake just a few months later. When questioned about this decision, Buffett acknowledged that TSMC was indeed an exceptionally cheap investment in October 2022, and he recognized its strength, profitability, and overall business as unmatched. Nevertheless, geopolitical risks, including the potential for a Chinese invasion, were among the reasons for Buffett’s divestment. He believed that TSMC would be at risk of destruction in the event of such an invasion, prompting him to seek an alternative company similar to TSMC but based in the United States.
However, it is important to examine the risks associated with a Chinese invasion and whether China would be willing to bear the immense expense of invading Taiwan. Wouldn’t it be more advantageous for China to focus on developing its own semiconductor market? As of December 2022, many experts considered a full-scale invasion of Ukraine to be highly improbable. Russia’s national security policy, rooted in the 18th century, aimed to expand its borders as far away from Moscow and St. Petersburg as possible, primarily due to the vulnerability posed by the Great European Plains through which France and Germany historically entered Russian territory.
Great European Plain (Wikipedia)
However, China’s formidable military and strong central government make it a challenging target for invasion. The motivation behind any potential invasion of Taiwan is not primarily existential but rather rooted in strategic and historical factors.
Indeed, the cost of invading Taiwan would be exorbitant, considering that Taiwan has significantly bolstered its defense capabilities, and allies such as Japan and South Korea have also fortified their positions. For China to execute an amphibious invasion, substantial logistical support would be required, leading to a costly conflict. Consequently, a large-scale invasion of Taiwan is not a viable option. However, China could opt to impose a blockade on Taiwan’s airspace and waters, allowing the Taiwanese government to continue functioning and permitting innocent traffic such as commercial airplanes and container ships. China would then leave the decision of forcefully breaking the blockade, along with the resulting economic repercussions, to the United States. This is why the U.S. has been augmenting its military presence in the Pacific. In any case, in my opinion, China would prefer to enforce a blockade rather than launch a full-scale invasion. In the event of a blockade, I anticipate that TSMC would still be able to operate normally.
The Semiconductor Market
The global semiconductor market is experiencing rapid growth driven by its widespread utilization across various industries, including electronics, automotive, and communications. This expansion is fueled by factors such as the increasing adoption of digital technologies, the popularity of emerging technologies like AI and IoT, and the demand for PCs and laptops in the work-from-home era. The development of smart cities and the rising popularity of electric vehicles also contribute to the heightened demand for semiconductors. Overall, the market is witnessing significant expansion due to a diverse range of applications and technological advancements.
Projections indicate that the semiconductor market is expected to grow at a Compound Annual Growth Rate [CAGR] of 12.28% from 2023 to 2032. As of 2023, the market size stands at approximately $664.2 billion, and if these projections come to fruition, it is estimated to reach a market size of $1.88 trillion in 2032.
Projections of the Semiconductor Market Size (2022-2032) (Author’s Calculations)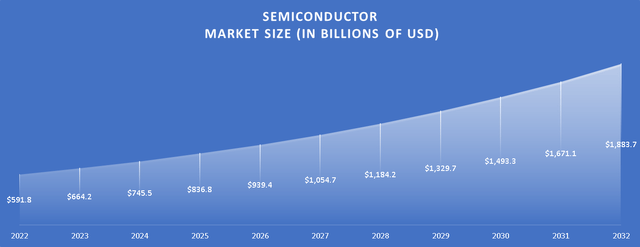
TSMC currently holds a substantial market share of around 54%, with Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. (OTCPK:SSNLF) being its closest competitor, holding a market share of approximately 10.9%. I consider Samsung as the only near-term threat to TSMC, as it has compelled some major companies to choose between TSMC and Samsung. For instance, Nvidia had to make a choice and initially opted for Samsung, but due to productivity issues, they eventually returned to TSMC. In response, Samsung announced its intention to compete with Nvidia in the arena of AI server processors. This highlights one of TSMC’s advantages, as it focuses solely on manufacturing and doesn’t produce its own chips.
Furthermore, the semiconductor market is currently experiencing a slowdown due to price decreases triggered by growing inventories. The main contributing factor to this slowdown is the declining sales of smartphones, cars, and PCs. These sectors are highly cyclical, as they depend on consumer purchasing power, which is being impacted by inflation. If there is a recession, it could present a significant buying opportunity for TSMC. An article published in April noted that TSMC had lowered its outlook in anticipation of this continued slowdown. Samsung responded by reducing production, leading to a 96% decline in profits. However, TSMC alone cannot solve the inventory issue. Designers need to reduce output, which directly affects TSMC as the contract manufacturer. The market is expected to begin recovering in the second half of 2023, with full recovery anticipated by 2024, driven by the demand for AI chips. Nevertheless, the key concern now is the duration of the recovery, as the lowest point may have already been reached when Samsung scaled back its production.
Financials (in millions of USD unless stated otherwise)
It is not surprising that TSMC has demonstrated remarkable revenue and net income growth. Since 2013, its revenue has increased by 278.6%, reflecting an impressive annual growth rate of 25%. Additionally, TSMC has achieved a strong net income after taxes of $33.4 billion.
Revenue & Income (Author’s Calculations)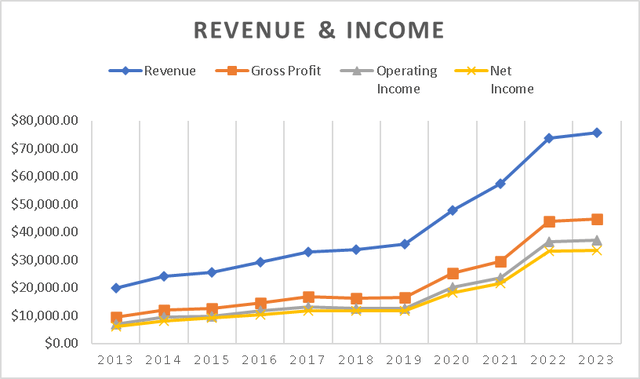
What is truly astonishing is the company’s high margins, considering its operation in a capital-intensive market. TSMC boasts a gross margin of 58.89%, a net operating margin of 48.82%, and a net income margin of 44.15%, which are close to its all-time highs. These figures indicate that TSMC is an exceptionally profitable business, and when examining the historical margins since 2013, we observe a consistent upward trend. However, I anticipate that as more companies enter the advanced-chips manufacturing sector, these margins may decline.
Furthermore, it is worth noting that TSMC currently benefits from an effective tax rate of approximately 11%, which is lower than the rates seen in the United States, for instance, where companies can pay over 20% of their profits in taxes. This potentially leaves room for a tax rate increase in the future.
margins (Author’s Calculations)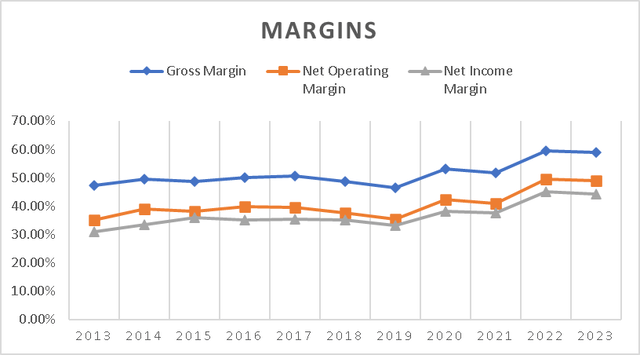
| Gross Margin | Net Operating Margin | Net Income Margin | |
| 2013 | 47.13% | 35.18% | 30.82% |
| 2014 | 49.51% | 38.92% | 33.34% |
| 2015 | 48.65% | 38.15% | 35.90% |
| 2016 | 50.09% | 39.87% | 34.99% |
| 2017 | 50.62% | 39.56% | 35.30% |
| 2018 | 48.53% | 37.58% | 35.20% |
| 2019 | 46.37% | 35.21% | 33.08% |
| 2020 | 53.10% | 42.31% | 38.14% |
| 2021 | 51.63% | 40.96% | 37.58% |
| 2022 | 59.56% | 49.56% | 44.90% |
| 2023 | 58.89% | 48.82% | 44.15% |
| Avg. | 51.28% | 40.56% | 36.67% |
When examining TSMC’s debt, it becomes apparent that it has been increasing since 2019. This rise in debt can be attributed to their efforts to diversify their manufacturing operations beyond Taiwan, with a particular focus on countries like the United States. The United States has shown keen interest in supporting TSMC’s expansion by enticing them to establish factories on American soil and offering financial assistance to facilitate this move. TSMC has already initiated its plan to invest $40 billion in constructing a new manufacturing plant in the United States, and they have recently deployed additional workers to accelerate the pace of construction.
According to the Pentagon, a Chinese invasion is not expected to occur at least until the end of the decade. This implies that TSMC has approximately seven more years to diversify its manufacturing away from Taiwan. However, such a shift would entail significant costs and result in TSMC taking on substantial amounts of debt, which could have adverse effects on their balance sheet.
Debt (Author’s Calculations)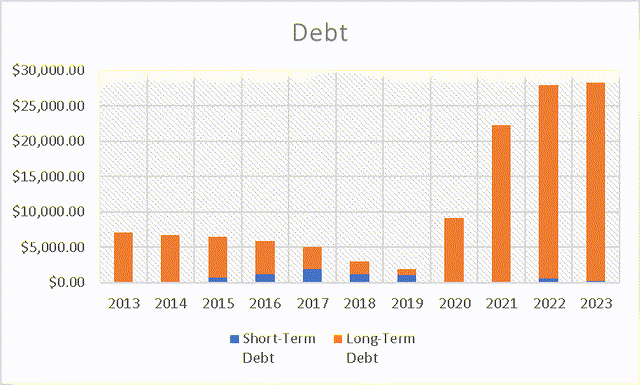
In the following graph, you can observe that TSMC has approximately 82% of its manufacturing plants located in Taiwan, 12% in China, and 6% in the USA. This distribution indicates that diversifying away from Taiwan within a seven-year timeframe would be practically impossible. To achieve such diversification, foreign governments interested in hosting TSMC plants would need to offer exceptionally favorable terms, including extremely low-cost debt and substantial assistance.
Factories Distribution by Country (Author’s Calculations)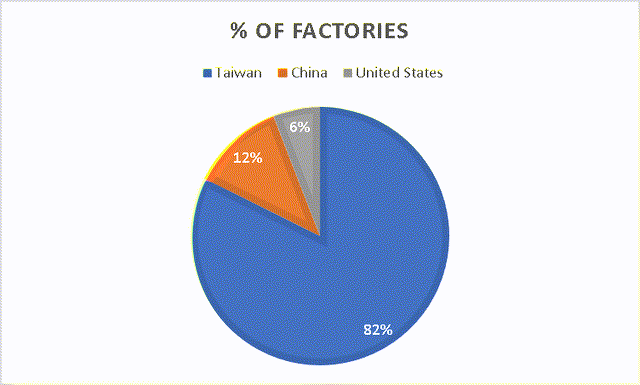
| Factories by Country | % of Factories | |
| Taiwan | 14 | 83.3% |
| China | 2 | 11.1% |
| United States | 1 | 5.6% |
Furthermore, TSMC’s overall free cash flow has witnessed a remarkable increase of 1,100% since 2013, representing an impressive annual growth rate of 100%. As of 2023, TSMC’s free cash flow stands at $12 billion.
Free Cash Flow Components (Author’s Calculations) Free Cash Flow Evolution (Author’s Calculations)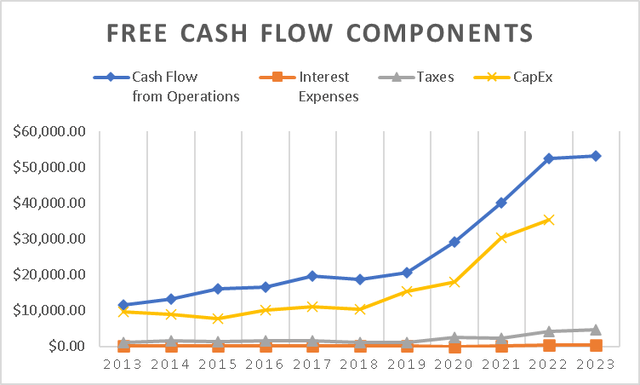
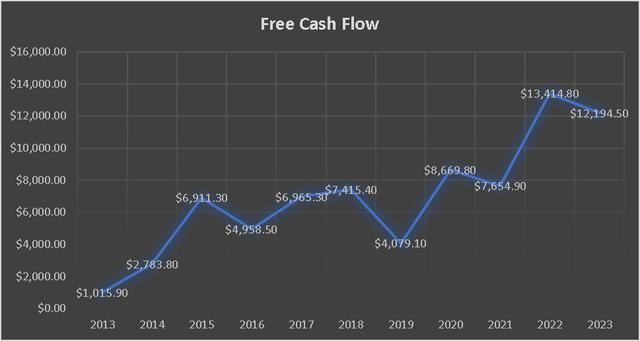
However, in this particular aspect, we observe an opposite trend compared to the operating margins, which were on an upward trajectory. The free cash flow margin has been experiencing a downward trend since 2019. The primary reason behind this decline can be attributed to the increased capital expenditures undertaken by TSMC since 2019. As mentioned earlier, these expenditures are part of TSMC’s efforts to diversify away from Taiwan.
Capital Expenditures (Author’s Calculations) Free Cash Flow Margin (Author’s Calculations)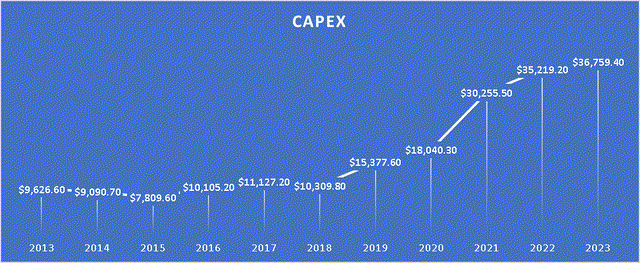
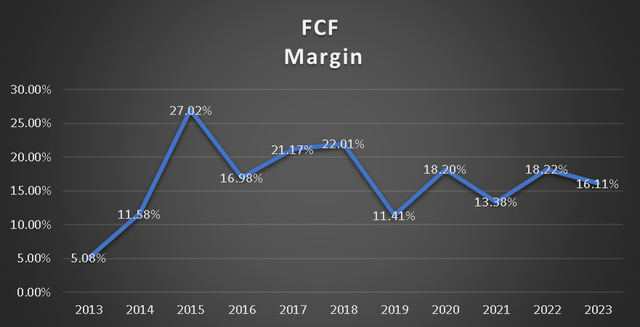
Overall, TSMC remains a highly liquid company with favorable operating margins, although the free cash flow margin has been on a downward trend. However, if TSMC decides to do so, it could potentially increase its free cash flow by reducing capital expenses. Nonetheless, at present, these expenses are vital for the company’s growth and even its continued existence.
Valuation (in millions of USD unless stated otherwise)
To value the TSMC stock, I will employ a Discounted Cash Flow [DCF] model. To begin, I need to project the revenue growth up to 2028. For the years 2023 and 2024, I will utilize the expectations provided in Seeking Alpha’s TSM Summary section.
For the years 2025 to 2028, I will assume a steady revenue growth rate of approximately 12% annually. The projected revenues are as follows:
| Revenue | |
| 2023 | $68,790.00 |
| 2024 | $83,180.00 |
| 2025 | $93,361.23 |
| 2026 | $104,807.32 |
| 2027 | $116,661.03 |
| 2028 | $130,975.33 |
Next, to calculate the net income after taxes, I will utilize the average net income margin from 2013 to 2023, which stands at approximately 36.6%. This approach takes into account the possibility of any future tax rate increases, as discussed in the “Financials” section.
| Revenue | Net Income | |
| 2023 | $68,790.00 | $25,225.29 |
| 2024 | $83,180.00 | $30,502.11 |
| 2025 | $93,361.23 | $34,235.56 |
| 2026 | $104,807.32 | $38,432.84 |
| 2027 | $116,661.03 | $42,779.60 |
| 2028 | $130,975.33 | $48,028.66 |
To determine the taxes, I will use a tax rate based on revenues, as this method has proven to be more accurate, considering the results obtained for 2023. This revenue-based tax rate is estimated to be around 6.7%, calculated by dividing the income tax expense by the revenue. It is important to clarify that the term “Plus taxes” does not imply that the taxes amount to $29 billion; the actual tax paid can be obtained by subtracting “Plus taxes” from “Net Income”.
| Revenue | Net Income | Plus Taxes | |
| 2023 | $68,790.00 | $25,225.29 | $29,829.29 |
| 2024 | $83,180.00 | $30,502.11 | $36,069.20 |
| 2025 | $93,361.23 | $34,235.56 | $40,484.08 |
| 2026 | $104,807.32 | $38,432.84 | $45,447.42 |
| 2027 | $116,661.03 | $42,779.60 | $50,587.53 |
| 2028 | $130,975.33 | $48,028.66 | $56,794.62 |
Furthermore, for depreciation and amortization (D&A) and interest expenses, I will also utilize proportions derived from the revenue. As mentioned earlier, when TSMC’s revenue increased, so did their capital expenditures. To finance these expenditures, TSMC utilized some debt, leading to the surge in debt levels post-2019. The proportion I have derived is that TSMC allocates approximately 0.60% of its revenue to interest expenses and 20.35% to D&A expenses.
| D&A Projection | Interest Projection | |
| 2023 | $13,997.80 | $411.50 |
| 2024 | $16,925.96 | $497.58 |
| 2025 | $18,997.70 | $558.48 |
| 2026 | $21,326.82 | $626.95 |
| 2027 | $23,738.88 | $697.86 |
| 2028 | $26,651.64 | $783.49 |
In the following table, you will be able to observe the projected EBITDAs for the period of 2023 to 2028:
| Revenue | Net Income | Plus Taxes | Plus D&A | Plus Interest | |
| 2023 | $68,790.00 | $25,225.29 | $29,829.29 | $43,827.09 | $44,238.59 |
| 2024 | $83,180.00 | $30,502.11 | $36,069.20 | $52,995.17 | $53,492.75 |
| 2025 | $93,361.23 | $34,235.56 | $40,484.08 | $59,481.78 | $60,040.26 |
| 2026 | $104,807.32 | $38,432.84 | $45,447.42 | $66,774.24 | $67,401.20 |
| 2027 | $116,661.03 | $42,779.60 | $50,587.53 | $74,326.41 | $75,024.27 |
| 2028 | $130,975.33 | $48,028.66 | $56,794.62 | $83,446.26 | $84,229.75 |
| ^Final EBITA^ |
Lastly, I completed the table of assumptions with the 2023 data available on Seeking Alpha. The Beta value was obtained from MarketWatch, and the market return was calculated based on the performance of the S&P 500 over the past 10 years.
Assumptions Table (Author’s Calculations) DCF Part 1 (Author’s Calculations) DCF Part 2 (Author’s Calculations)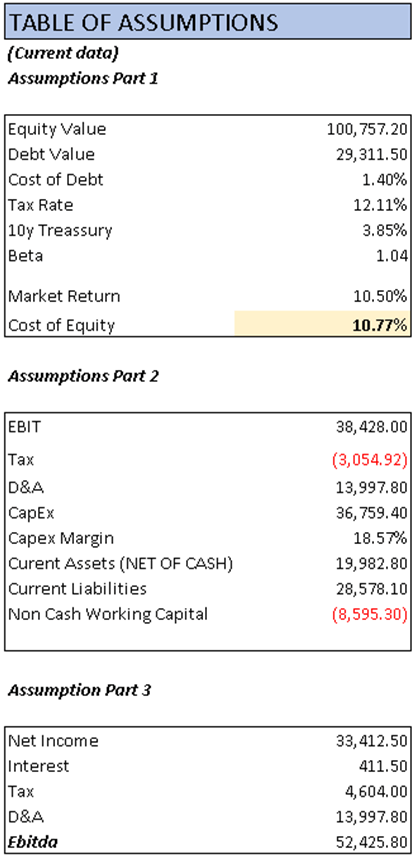
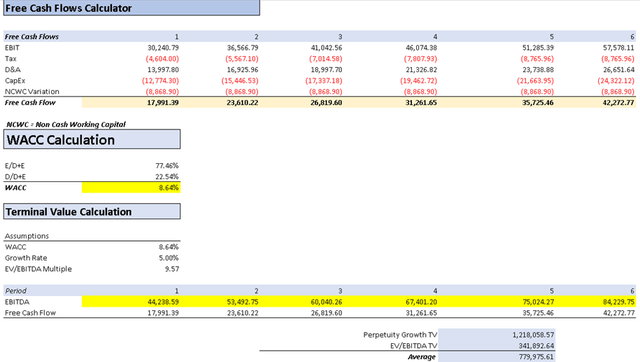
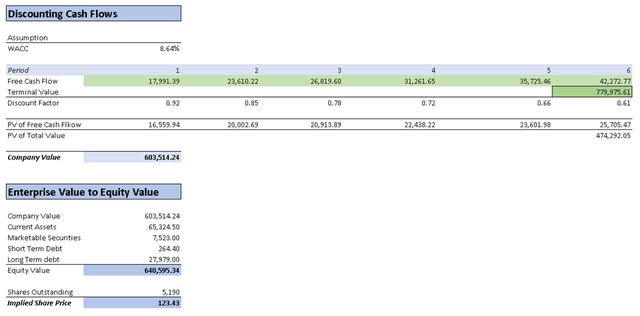
The DCF analysis resulted in an intrinsic value per share of $122.43, which represents an approximate 22% increase compared to the current stock price of $100.23. It may appear high, but it’s important to consider that this calculation takes into account 5 years of future cash flows. Moreover, the implied share price could have been higher if I had extended the projection until 2032.
Finally, to estimate the stock price for the future, I projected this present implied stock price forward, which is the reverse of discounting. This projection suggests a stock price of $184.52 for 2028, indicating a potential increase of around 84% compared to the current stock price of $100.23. This implies an annual return of 14%, which could be even higher if TSMC reduces its capital expenditures or achieves better revenue figures.
Risks to thesis
I anticipate that TSMC will maintain its dominant position in the market, with United Microelectronics Corporation (UMC) being the only significant player I see as a relevant competitor since it is another major contract chipmaker. Other competitors such as Intel and Samsung are involved in both chip design and production, which is the same reason why TSMC was established – to avoid reliance on Integrated Device Manufacturers (IDMs) that act as both manufacturers and competitors.
The greatest risk I identify lies in the China-related factors. Any invasion of Taiwan would result in the complete destruction of TCMC’s business, given that 82% of their plants are located in Taiwan. Consequently, TSMC is actively seeking to rapidly diversify its manufacturing to other countries. However, this expansion is likely to require increased reliance on debt.
Another risk to consider is market sentiment, which plays a crucial role in valuation. Currently, the concern centers around declining chip prices and whether the recovery can be achieved by 2024. This issue will likely have an impact on TSMC’s upcoming earnings on July 13. It is challenging to predict whether TSMC will lower its outlook, as the recovery depends significantly on the demand for AI chips and whether they can compensate for the decreased sales in PCs, cars, and smartphones, which constitute a significant portion of TSMC’s contracts.
Nevertheless, I firmly believe that TSMC is a “buy” due to its unique ability to manufacture highly advanced chips. Even if they were to reduce their outlook, they would still remain an excellent company, and their long-term prospects make them a worthy investment.
Conclusion
TSMC stands out as a prominent contract chip manufacturer, exhibiting robust financial performance and enjoying a substantial market share. The company has achieved remarkable revenue and net income growth, accompanied by impressive profit margins. However, it is essential to consider certain risks, such as the potential impact of a China invasion and the necessity of diversifying manufacturing operations away from Taiwan. TSMC’s ability to effectively address these challenges will be pivotal for its future success. Furthermore, market sentiment and the recovery of chip prices will significantly influence TSMC’s performance in the coming years. Nevertheless, despite these risks, TSMC’s specialization in advanced chip manufacturing and its dominant market position make it an appealing investment opportunity, particularly with the potential for further buying opportunities emerging from any adjustments in their outlook. Based on a DCF model, a projected stock price of $184.52 for 2028 indicates an upside of approximately 84%.
Read the full article here


